|
In
Sunni -
Islam
-
x articles of faith (Sunni Islam)
-
Five roots of Usul ad-Din (Shi’a Islam)
-
Nature of God
-
Imamate (Shi’a Islam)
-
Risalah (prophethood)
-
The prophets before Muhammad
-
Muhammad
-
Books (kutub)
Islam, there are six main
articles of faith. These are based on statements in the Qur’an:
Oh you who have believed, believe in Allah and His Messenger and the
Book that He sent down upon His Messenger and the Scripture which He
sent down before. And whoever disbelieves in Allah, His angels, His
books, His messengers, and the Last Day has certainly gone far astray.
— Surah 4:136
Eduqas-specific spelling in a visualisation of the six articles of Sunni
Islam.
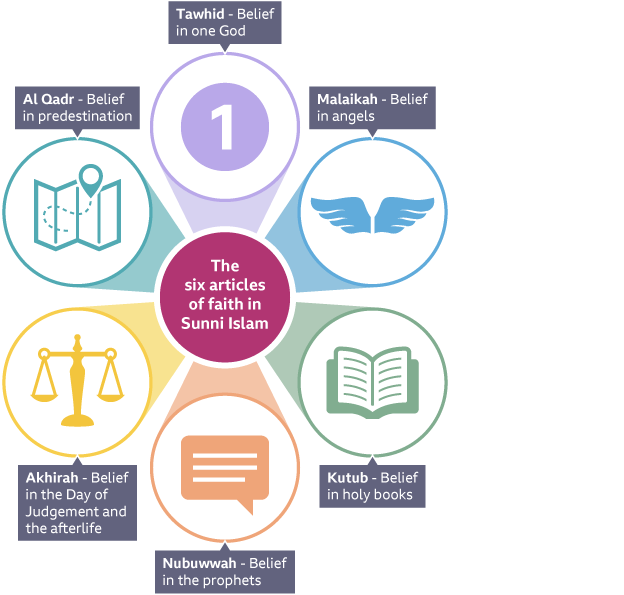
Belief in one God (Tawhid) This
means having absolute faith in the oneness of God. Allah is simply the
Arabic word for God. It has no plural in Arabic, which shows that there
is only one God. Muslims believe that no being is like Allah.
Belief in angels (malaikah) Angels were the first creation of God.
Muslims believe that God’s greatness means he does not communicate
directly with humans and so he passed messages (risalah) to his prophets
via the angels. Angels also tell Allah about the behaviour of humans.
Belief in holy books (kutub) The holy books of Islam should be
respected. This is especially true of the Qur’an, which is the unchanged
word of Allah, revealed to the Prophet
Muhammad
Belief in the prophets (nubuwwah) Allah is believed to have communicated
with the prophets, called nubuwwah, through the angels. Muslims believe
the prophets should be respected but never worshipped.
Belief in the Day of Judgement and the afterlife (Akhirah) Muslims
believe that life on Earth is a test and that, after they die, they will
be judged by God and sent to either Paradise or Hell.
Belief in predestination (Al-Qadr) This means that everything in the
universe follows Allah’s masterplan – Muslims believe that Allah has
decided everything that happens. This shows the importance of God’s
will: In all things the master-planning is God’s (Surah 13:42). The
Prophet Muhammad also told his followers: There is not one amongst you
who has not been allotted his seat in Paradise or Hell (Sahih Muslim,
Book 33, Hadith 6400). Muslims take this as further proof that every
person’s life is already mapped out in Allah’s plan.
Risalah (prophethood)
Risalah
is the Arabic word for ‘message’. It refers to ‘prophethood’ and
represents the various ways Allah communicates with humanity to reveal
his messages.
Risalah as revelation
Islam teaches that Allah wants to help people live good lives, so he
sends messages to guide them. This is called revelation . Many of these
messages are found in the Qur’an
. Muslims believe that revelations from Allah were communicated through
prophets
.
Key fact
The prophets are not worshipped because Allah is the one true God.
Instead, they are respected.
The prophets are the connection between Allah and humanity.
There are 25 named prophets in the Qur’an, although many people believe
there may have been as many as 124,000.
All of the prophets are considered to be equal: We make no distinction
between any of them (Surah 2:136).
Allah chose the prophets to reveal his truth. They are responsible for
the revelation.
Messages from Allah were sent to the prophets using angels (malaikah).
These messages are recorded in the holy books.
The prophets performed miracles, which proved they really were prophets.
In the Qur’an, Allah warns against ignoring the messages given by the
prophets:
Those who disbelieved from among the Children of Israel were cursed by
the tongue of Dawud [David] and Isa [Jesus], the son of Maryam [Mary]:
because they disobeyed and committed excesses.
— Surah 5:78
All of the prophets received the same message about
there being one God, which shows that Allah is unchanging and that Islam
is the true religion. Muslims believe that
Muhammad was the final prophet.
The prophets before Muhammad
Key fact
Islam, along with Judaism and Christianity, is known as an Abrahamic
religion. These three religions originate from the Prophet Abraham, who
is known as Ibrahim in Islam.
Ibrahim is believed to have been the first person to teach the idea that
there was only one God. Before then, people had strayed into believing
in many gods.
Islam, Judaism and Christianity share a focus on key figures, including
many
prophets
. The
Qur’an
says: Of some messengers we have already told you the story; of others
we have not, and to Musa [Moses] God spoke direct (Surah 4:164).
Some of the most important figures who appear in the scriptures of all
three Abrahamic religions are as follows.
Adam
Adam was the first human being and he is believed to have been the first
prophet.
Muslims believe he was created from clay by Allah and given the ability
to think logically as well as the role of
khalifah
.
Muslims learn about their role on Earth from the example of Adam, who
was forgiven for his
sin
.
Some Muslims believe that Adam built the
Ka’ba
, which they believe was the first ever place of Muslim worship.
Muslims believe that Adam was given knowledge to pass on to the rest of
the human race.
Ibrahim
Ibrahim is regarded in Islam as the father of the Arab people.
In Ibrahim’s time, people practised idolatry. Ibrahim refused to worship
idols and would only worship one God, Allah. He is known as a hanif,
which is a person who lived before
Muhammad
and who was totally committed to worshipping only one God.
It is believed that Ibrahim rebuilt the Ka’ba following the great flood.
His faith was tested by Allah, which teaches Muslims that they must be
prepared to submit to Allah in the same way.
Isma’il (see below) was one of Ibrahim’s sons.
Isma’il
Isma’il was the first son of Ibrahim.
He is associated with Makkah (Mecca) and the building of the Ka’ba.
Musa
Musa taught that there is one God at a time when Muslims were practising
idolatry.
Musa is thought to have been the only prophet that Allah spoke to
directly.
Musa is known as Moses in Judaism and Christianity.
Dawud
Dawud is known for his bravery and wisdom.
The Qur’an states that Dawud killed Jahut, known in the Bible as
Goliath, and that because of this, God made him a king (Surah 2:251).
He received the Zabur, a book of psalms, which was revealed by God.
He is called David in Judaism and Christianity.
Isa
Isa is an important prophet in Islam. He was born miraculously to the
most admired woman in Islam, Maryam (Mary), who was a virgin.
Isa is known as Jesus in Christianity. However, in contrast to
Christians, Muslims do not believe that Isa was crucified and
resurrected, or that he was the son of God.
Muslims believe that the Prophet Isa will return to Earth just before
the Day of Judgement
.
Muhammad
Muslims believe in one God, Allah, and follow the teachings of the
Prophet Muhammad , Allah’s messenger.
Key fact
Muslims believe that the Prophet Muhammad received the Qur’an , which is
the most important Islamic holy book and the only one to contain the
pure word of Allah.
Muhammad as the Seal of the Prophets
In AD611, the Prophet Muhammad was meditating in a cave when the Angel
Jibril appeared to him. This is known as the Night of Power. Muhammad
could not read but three times Jibril ordered him to ‘proclaim’ or
recite Allah’s message. The angel said:
Proclaim! In the name of thy Lord and Cherisher, who created – created
man, out of a [mere] clot of congealed blood. Proclaim! And thy Lord Is
Most Bountiful! He who taught [the use of] the pen taught man that which
he knew not.— Surah 96:1–5
Jibril then told Muhammad that he was to be the messenger of Allah.
These revelationscontinued for the next 23 years.
Muhammad is the final prophet in Islam, known as the ‘Seal of the
Prophets’. This means that Muslims regard Muhammad as Allah’s final
messenger. The Qur’an is formed from the revelations Muhammad received
from God through the Angel Jibril. Muslims do not believe that Muhammad
was in any way divine, and this is confirmed in the Qur’an, which
states: Muhammad is no more than a messenger (Surah 3:144).
According to Islamic belief, no further prophets will come after
Muhammad, as he communicated Allah’s final message to humankind: Say, [O
Muhammad, to humankind]: If ye love Allah, follow me; Allah will love
you and forgive you your sins. Allah is Forgiving, Merciful (Surah
3:31).
Books (kutub)
Muslims believe that Allah revealed holy books to other prophets who
came before
Muhammad
. These books are called ‘revealed’ books, or
kutub
, meaning that Muslims believe they originally contained the same
message as the
Qur’an
.
And We sent … Isa [Jesus], the son of Maryam [Mary], confirming that
which came before him in the Torah; and We gave him the Gospel, in which
was guidance and light and confirming that which preceded it of the
Torah as guidance and instruction for the righteous.
— Surah 5:46
The Qur’an
According to Islamic belief, the meaning of the books revealed by God
prior to the Qur’an has become unclear, because Allah’s word has been
mixed with texts created by people. Therefore, only the Qur’an is
accepted as the true word of Allah. In Surah 5:48, Muslims find the
following teachings about the
revelation
of the Qur’an:
The Qur’an was revealed to Muhammad as God’s truth.
The Qur’an confirms the revealed books that came before it but takes
priority over all of them. Where any of the other scriptures appear to
be
contradictory
to the Qur’an, the teaching in the Qur’an is correct.
The Qur’an sets out how people should live, and other incorrect
scriptures and teachings exist to test people’s faith.
The Qur’an is regarded as the final revelation from Allah to the Prophet
Muhammad. It was revealed to him in Arabic. The Qur’an is therefore
different from any other book for Muslims because it contains the direct
and final revealed words of Allah.
Image caption,
The Qur’an is the main holy book in Islam
Revealed books prior to the Qur’an
Sahifah
The Sahifah contains the scrolls of Ibrahim (Abraham), also known as ‘Suhuf’.
These are part of the early religious scriptures of Islam. It is
believed that they are now lost, but contained Allah’s revelations to
the Prophet Ibrahim, which were written down by him and his followers.
The Tawrat
The Tawrat is known by Jews as the Torah
. It is the holy book revealed directly by God to the Prophet Musa. This
book contains the Ten Commandmentsand sets out the ‘judgement of Allah’
on non-believers.
Zabur
The Zaburcontains psalms, or poetic prayers of praise and worship. They
are mentioned in the Qur’an as being revealed to King Dawud and are
similar to those found in the Christian Bible. The Qur’an states: We
sent inspiration to Ibrahim [Abraham], Isma’il, Ishaq [Isaac], Ya’qub
[Jacob] and the Tribes, to Isa [Jesus], Ayyub [Job], Yunus [Jonah],
Harun [Aaron], and Sulayman [Solomon], and to Dawud [David] We gave the
Psalms (Surah 4:163).
Injil
Injil is a book believed to have been given by God to the Prophet Isa
(Jesus). It is sometimes referred to as the Gospel of Jesus in Islam.
Muslims believe that the meaning of this book has been altered by people
over time, like all of the holy books prior to the Qur’an. Rather than
teaching that Isa was the son of God, as in Christianity, Muslims
believe that the Injil reveals the coming of the Prophet Muhammad.
 |
|
There are five key
principles of faith in Shi’aIslam, known as the five roots of Usul
ad-Din. The image of a tree with five roots is often used to show that
these principles are the foundations of the faith.
Eduqas-specific spelling in a visualisation of the Shi'a Islam five
roots of faith
.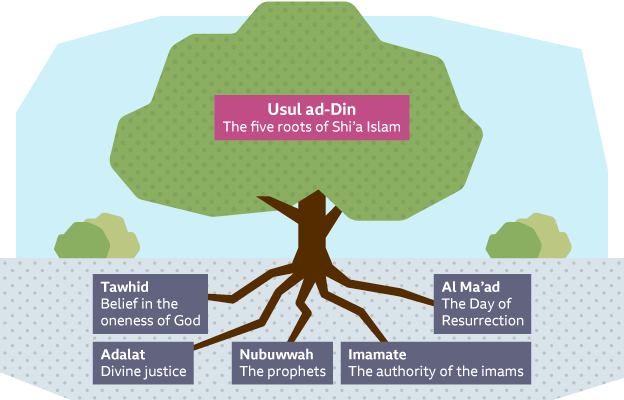
Tawhid
Tawhid
is the belief that God is one and that he is almighty and worthy of
worship. The Qur’an states that God cannot be
thought of as having separate parts:
He is the Originator of the heavens and the earth. How could He have a
son when He does not have a companion and He created all things? And He
is, of all things, Knowing.
— Surah 6:101
Adalat (divine justice)
Shi’a Muslims believe that Allah is always right and fair (Adalat).
Sometimes Allah may act in ways that are beyond human understanding, but
ultimately the world has been designed to be fair. The Qur’an teaches
that God will not burden anyone with more than they can bear because he
is fair to everyone (Surah 23:62).
Muslims believe that there will be a Day of Judgement, where they will
prove their faith and take responsibility for their actions on Earth.
The Qur’an explains that all good deeds benefit the soul, but each
person is also responsible for the things that they have done wrong.
Allah will always judge people with justice and fairness (Surah 41:46).
Nubuwwah (the prophets)The prophets, known as nubuwwah, provide guidance
from God and should be respected. The Prophet Muhammad
was God’s final prophet and communicated the Qur’an to human beings.
The Qur’an says the following about the messengers who were sent by God:
They were sent to stop humankind from straying from Islam and to bring
good tidings and warnings (Surah 2:213).
They were sent into all communities to tell people “to worship Allah and
shun false gods” (Surah 16:36).
They were sent to educate people who couldn’t read or write (Surah
62:2).
They were sent with proof, scripture, the ‘scales of justice’ and the
‘might of iron’ to see who would stand up for Allah and his messengers
without ever having actually seen Allah for themselves (Surah 57:25).
Imamate (authority of the imams)
The Imamate were the Twelve Imamswho Shi’a Muslims believe were chosen
by God to lead Islam after Muhammad. Shi’a Muslims believe that leaders
such as imams protect the religion and help to guide Muslims along the
right path. They also believe that the Qur’an is referring to imams when
it says:
We [God] made them leaders guiding by our command, and inspired them to
do good deeds, establish prayer, and pay alms-tax. And they were devoted
to Our worship.
— Surah 21:73
The prophet Muhammad is recorded by some Hadithauthors as saying that he
leaves behind ‘two weighty things': the Qur’an and his household. This
is often referred to as the Hadith al-Thaqalayn. Shi’a Muslims see this
as evidence that authority should be passed to the imams, the Prophet’s
descendants.
Al-Ma’ad (Day of Resurrection)
Al-Ma’ad is the belief that Muslims will be
resurrected and judged by God: As We began the
first creation, We will repeat it. [That is] a promise binding upon Us.
Indeed, We will do it (Surah 21:104).
The Qur’an tells Muslims that people who have lived good lives will
receive a record of their life in their right hand as a token of their
faith. They will go to Heaven. Those who have not offered prayers or
helped the poor, and people who have told lies, will be condemned to
Hell.
Nature of God
Allah is the Arabic word used by Muslims for God. All Muslims believe
that Allah is the one true God, and only Allah is worthy of worship.
Muslims believe that, as the supreme being who created and
sustains
the world, Allah should be treated with the utmost respect and given
praise.
Do they not see that Allah, who created the heavens and earth and did
not fail in their creation, is able to give life to the dead? Yes.
Indeed, He is over all things competent.
— Surah 46:33
Tawhid
Tawhid
is the word used to express the Islamic belief in the oneness of Allah
(God). Muslims believe that there is only one God, who is not divided in
any way into parts: Allah Himself witnesses that there is no God except
Him (Surah 3:18)
Affirming the belief that Allah is the one and only God forms the first
part of the
Shahadah
.
Shirk means believing in more than one God or holding up anything or
anyone as equal to Allah. This would also include claiming that God can
be divided into parts or persons. For example, Muslims could never
accept the Christian doctrine of the Trinityor any form of polytheism .
Muslims believe that shirk is the worst of all sins
.
The characteristics of Allah
The opening surah of the Qur’an, called the Surah Al-Fatihah, tells
Muslims that Allah is:
the Most Beneficent, which means the most loving
the Most Merciful
the Lord of everything that exists – in Arabic, Alamin
the only one worthy of worship
the only owner of the world and everything in it, and the only ruling
judge
the only divine source of help and guidance
one who blesses people who follow him and please him, and punishes
people who do not
Additionally, Muslims believe that Allah is:
Transcendent– Allah is above and beyond everything that exists in the
world.
Fair and just – Allah judges everyone equally.
Immanent– Allah is close to every human and exists in all things on
Earth. The Qur’an states that God, having created human beings, knows
what his [each person’s] soul whispers to him, and [is] closer to him
than [his] jugular vein (Surah 50:16).The omnipotent creator – The
Qur’an states that Allah is the originator of the heavens and the earth.
When He decrees a matter, He only says to it, ‘Be,’ and it is (Surah
2:117).
Forgiving.
Muslims believe that Allah has shown 99 characteristics (sometimes
called attributes) to human beings to help them better understand his
nature, eg “He is Wise” or “The Great Forgiver”. Muslims call these
attributes the 99 names of Allah. Some Muslims use subhah when
praying to remember these names.
Imamate (Shi’a Islam)
Imamate is a Shi’abelief that all imamsshould be spiritual descendants
of the Prophet Muhammad. Shi’a Muslims believe that imams are leaders
appointed by God to be Muhammad’s successors.
Key fact
Shi’a Muslims believe that imams are inspired by God, are without sin
and are infallible, which means that they can interpret the teachings of
the Qur’an without making any errors.
Today, Shi’a Muslim communities are led by imams, who are seen as having
been chosen by God. Imams should be exemplary individuals who obey all
teachings and follow
Shari’ah law.
Origins of Imamate
After the Prophet Muhammad
died, the Muslim community had to choose a successor
. Abu Bakr, who was Muhammad’s father-in-law and closest friend, became
the leader of the Sunni Muslim community.
Sunni Muslims, who make up around 90 per cent of the global Muslim
population, agree that the rightful successor to Muhammad was Abu Bakr,
Muhammad’s father-in-law. They recognise two further leaders who came
after Abu Bakr. They then recognise a fourth leader, Ali (Muhammad’s
cousin). Sunni Muslims accept all four leaders, including Abu Bakr and
Ali, as the rightful successors of Muhammad.
Shi’a Muslims, also called ‘the party of Ali’, believe that Muhammad
chose Ali as his successor rather than having a bloodline successor.
After Ali’s death, Shi’a Muslims were led by twelve imams, whom they
believe were spiritual successors to the Prophet Muhammad rather than
having any family connection to him. This was the beginning of the
Imamate. Shi’a Muslims make up around 10 per cent of the global Muslim
population.
The Twelvers
The Twelvers is a branch of Shi’a Islam whose followers believe that
there were twelve imams after the death of Muhammad. The twelfth imam,
however, has been kept alive by God and is hidden somewhere on Earth.
Shi’a Muslims believe the twelfth imam will one day make himself known
and bring equality to all.
Shi’a Muslims believe that the imams are necessary because people need
guidance on how to live correctly. Due to their close relationship with
God, the twelve imams are highly respected.
Isma’ili Shi’a Muslims
Ismai’ili Shi’a Muslims, sometimes known as the Seveners, believe that
the seventh imam was Isma’il. Isma’il was the son of one of the Twelve
Imams. Seveners believe that each imam can choose his successor, as they
believe the last hereditary imam was Isma’il.

|


