NATURE - PLANTS AND TREES
大自然中的城市每年 5 月 14 日的世界候鸟日

![]()
|
NATURE
|
| Zingiberales |
|
|
兰花分类学
|
orchids |
|
LITTLE RED DOT
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
在短短不到六十年的时间里,新加坡也迅速华丽转身,从原来的一个平凡的小渔村,成为兼具Jiān jù国际地位和经济实力的“花园城市“。而如今的新加坡,已经不在满足于已经达成的“花园城市“的称号,它又有了更进一步的目标--”花园中的城市“,相信大家通过这几天的旅程,已经可以感受到新加坡在这方面所做的努力和已经取得的成果。
黄循财总理:大自然中的城市
让绿化也能在高楼大厦上出现-垂直绿化改善居住环境。 也改善城市生态环境,让更多的动物以及鸟类,栖息Qīxī和选择这座城市。
目标2030年! |
|
||||||||||||||||||
姜目 (Zingiberales)植物共有8大科:
++++++++++++++++++++++++++
同时,也是—些非洲国家的主要食品。除此,也用于观赏及生活用途上。
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
形態特徵
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
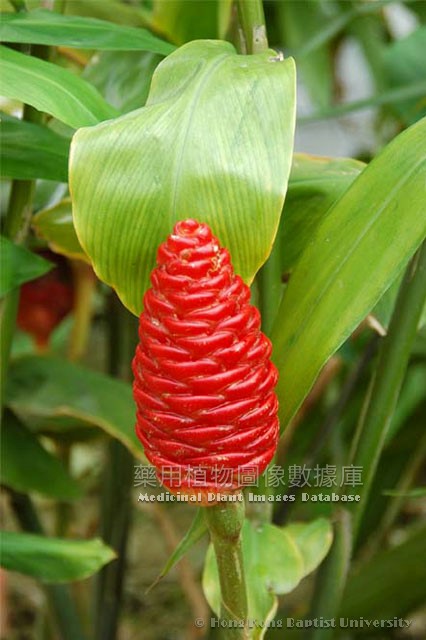
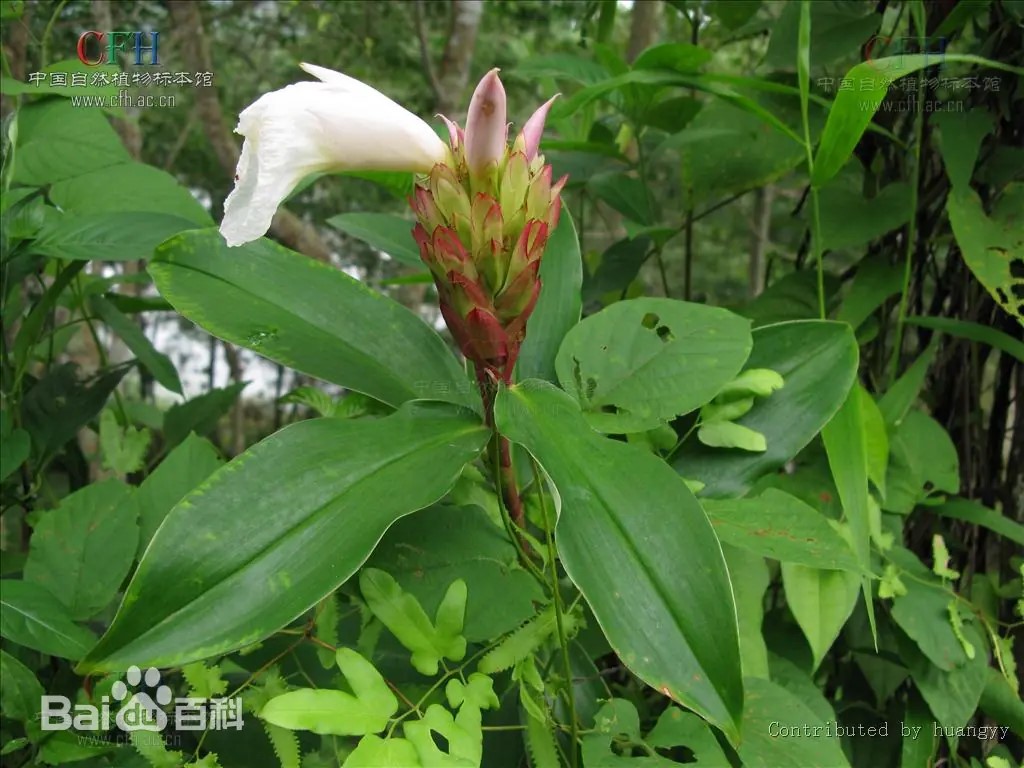
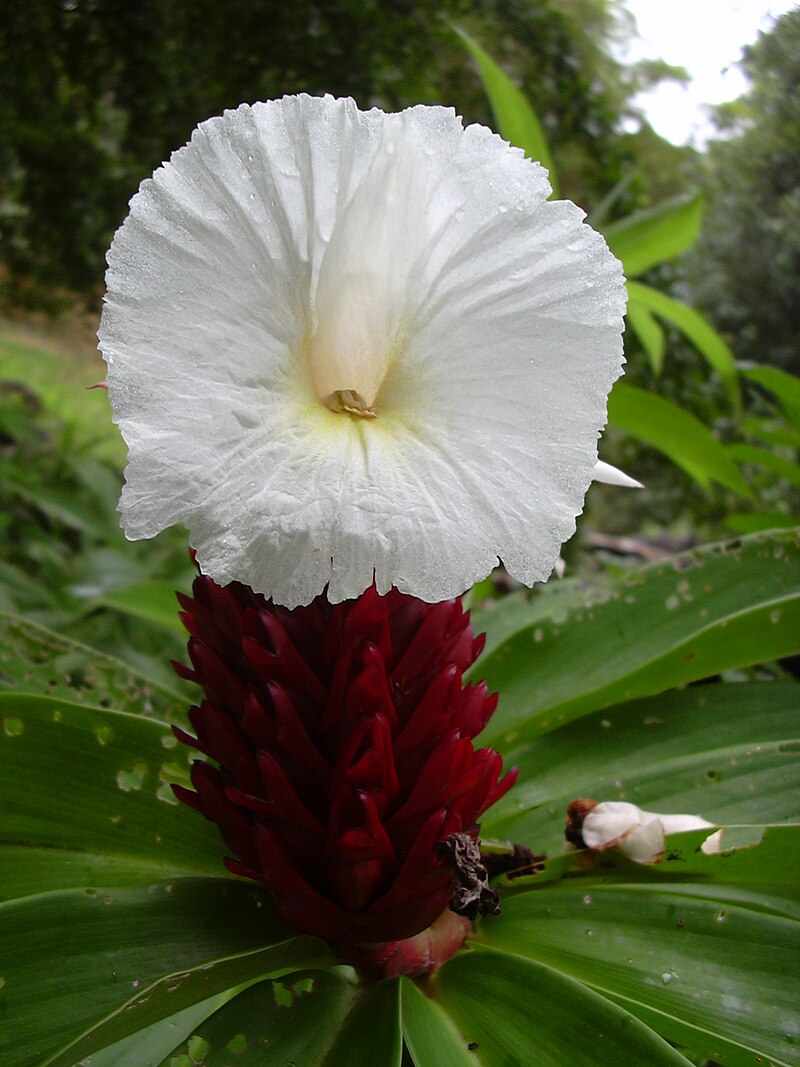
姜科 (Zingiberaceae)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Costaceae, known as the Costus family or spiral gingers, is a family of pantropical monocots. It belongs to the order Zingiberales, which contains horticulturally and economically important plants such as the banana (Musaceae), bird-of-paradise (Strelitziaceae), and edible ginger (Zingiberaceae). The seven genera in Costaceae
together contain about 143 known species[2] (1 in Monocostus, 2 in
Dimerocostus, 16 in Tapeinochilos, 2 in Paracostus, c. 8 in Chamaecostus,
c. 5 in Hellenia, and c. 80 in Costus).[3] They are native to tropical
climates of Asia, Africa, Central America, and South America. Several
species are frequently found in cultivation.[citation needed]
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
赫蕉科(Heliconiaceae)是
火紅赫蕉 Heliconia
bihai
金鳥赫蕉 Heliconia
rostrata
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
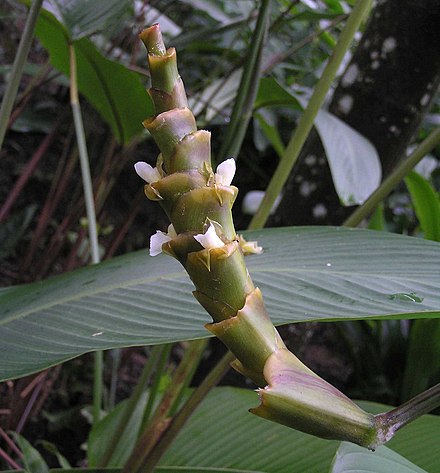
Lowiaceae
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
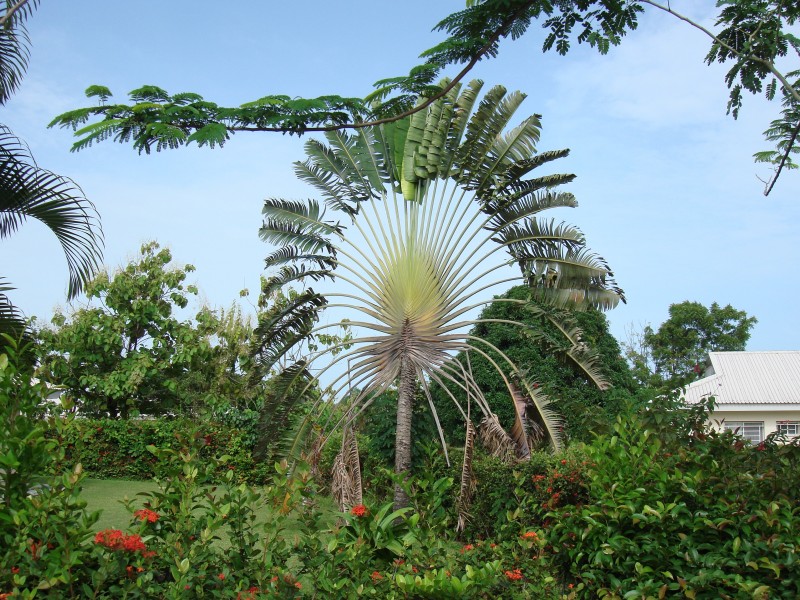
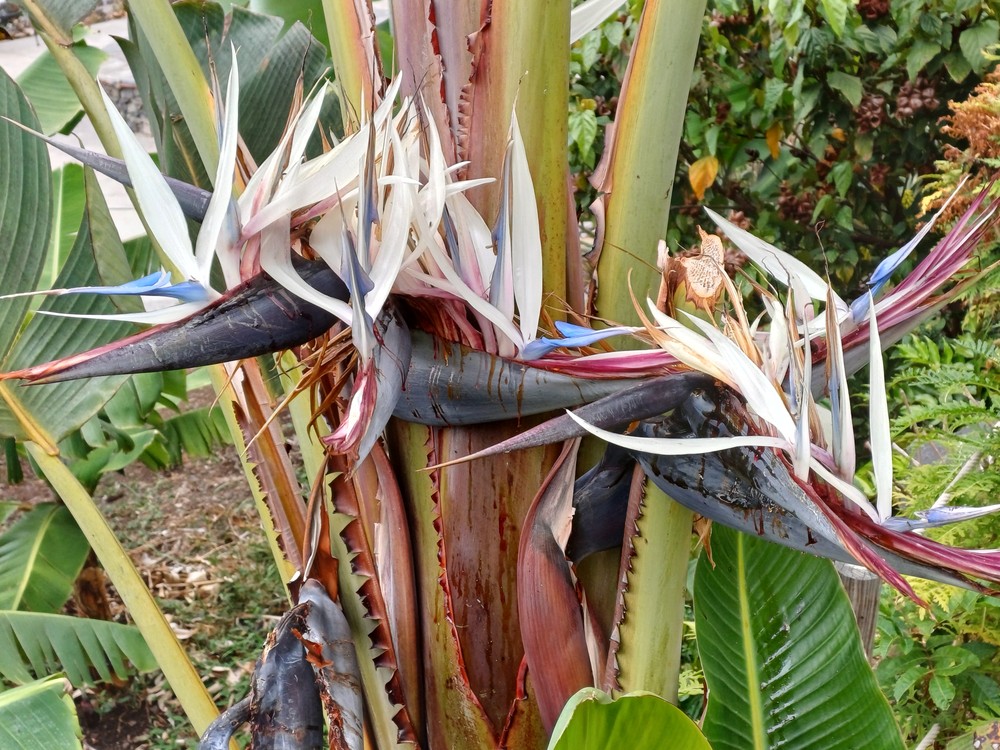
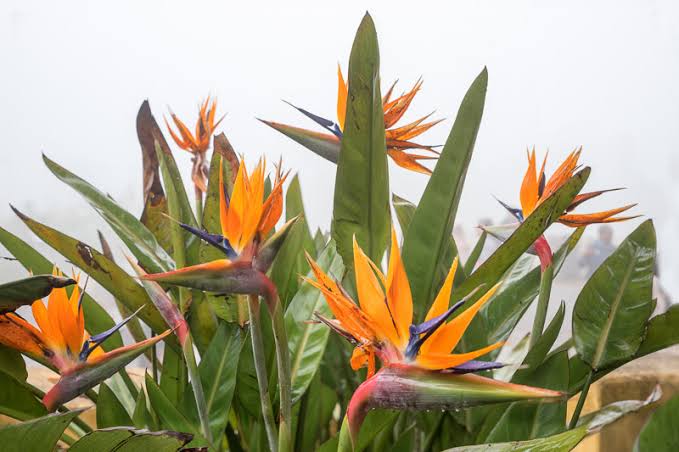
Strelitziaceae, family of flowering plants in the ginger order (Zingiberales), comprising three genera and seven species in tropical to subtropical regions. Several are cultivated as ornamentals in warm climates.
Though it's native to warmer regions like South Africa, bird of paradise (Strelitzia) can also be grown indoors as a houseplant. "Strelitzias
generate incredibly striking flowers, resembling an exotic bird ready to
take flight when blooming," Sword says, which is why bird of paradise
plants are usually linked to freedom. In order to bloom, Strelitzia
plants need bright light (including a few hours of direct light). Keep
the soil consistently moist, and mist daily to boost humidity. In ideal
conditions, bird of paradise plants can grow 5-6 feet tall, so make sure
you've got plenty of space. The bird-of-paradise flower (S. reginae), the white bird-of-paradise (S. alba), and the giant white bird-of-paradise (S. nicolai) are cultivated to various degrees for their unusual flowers and attractive foliage. Mountain strelitzia (S. caudata), which grows to more than 5 metres (16 feet) in height, has banana-like fruit and resembles the traveler’s tree. The rush-leaved strelitzia, or narrow-leaved bird-of-paradise, (S. juncea) has long needlelike leaves and is somewhat frost resistant. Genera and species-traveler's tree (Ravenala madagascariensis). Ravenala
madagascariensis, the ornamental traveler’s tree,
is the only member of its genus.
The plant is native to Madagascar and has a
palmlike trunk and leaves with
the appearance of a fan. The water that is stored in the leaf
bases may enable it to withstand dry conditions.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
在你们前方,就是国家兰花园,面积达到3公顷。这个花园是植物园的亮点之一,展示了1000多种胡姬花和2000多种配种品种,堪称世界上最大的胡姬花收藏地,拥有60000株胡姬花。国家兰花园于1988年建成,并在1995年由李光耀资政主持了开园仪式。它同时也是世界上最大的热带兰花展示区。发挥了“新加坡大使”的作用。 国家兰花园由著名的日本设计师稻田纯一郎设计,园区的布局以四季为主题,分为春、夏、秋、冬四个区域,以不同的颜色代表不同的季节: • 春季:青黄、淡橙及粉红色 • 夏季:艳红及金黄色 • 秋季:棕红色 • 冬季:白色及紫兰色。 一座钟楼 大家请看你们前面的这一座钟楼,高3.5米,底座厚达0.7米,由花岗石制成。为纪念1998年植物园游客中心的开放,陆婉平女士委托翁锡礼先生设计了这座雄伟的钢制艺术,他的设计灵感来源于新加坡植物园标准上优雅的口红棕榈。上面4个钟代表4个城市的时间(新加坡,东京,伦敦,温哥华) 胡姬花的基本特征是由 三个花瓣和三个花萼组成,或者 由三个花萼、两个花瓣和一个唇组成。 根据生长环境,胡姬花可分为附生(依附在树木上)和陆生(生长在地面)两种类型。而它们的茎部又分为单茎和多茎。 1.石斛兰 现在你们面前的就是石斛兰,属于复茎兰花 2.文心兰 在你们面前黄色花朵像舞裙的它就是被誉为“舞蹈女郎”的金色舞蹈胡姬花文心兰。这种胡姬花是配种品种,花朵的形状宛如身着舞会礼服的舞蹈女郎,因此它得到了“舞蹈女郎胡姬花”这一别名。 3.蜻蜓兰 在你们面前的黄色花朵像蜻蜓的就是蜻蜓兰,属于单茎兰花
是世界上最大的胡姬花收藏地,拥有超过60,000株植物和胡姬花。
自1928年开始的胡姬花育种计划所培育出的品种,理应有一个展示其绚丽风采的场所。
这些胡姬花的设计可以说是由植物园的园艺人员“精心打造”的,他们致力于从配种品种中培育出最优质的品种。
为纪念1998年植物园游客中心的
巳开放,陆婉平女士委托翁锡礼先生设计了这座雄伟的钢制艺术品,他的设计灵感来源于新加坡植物园标志上优雅的口红棕桐。 这一传统通过为新培育的胡姬花配种品种命名,向杰出的来访者致敬。 园中展示了以许多知名人士命名的胡姬花,每株胡姬花旁都配有铭牌,详细介绍这些人物及其对应的胡姬花品种。
它是由园艺高手,居住于新加坡的亚美尼亚人艾妮丝卓锦小姐, 1893年,植物园首任园长亨利·尼古拉斯·里德利Hēnglì·nígǔlāsī·lǐ dé lì确认它是新配种品种,
并以卓锦小姐的名字命名。花园开始栽培这种胡姬花,并很快在整个马来亚地区流行起来。 这种被称为金虎兰(Grammatophyllum speciosum)的胡姬花,每朵花可长到10厘米10 Límǐ/ CM 宽!
金虎兰因其色彩鲜艳的花朵而得名,花朵上的斑纹就像老虎的皮毛一样。
馆内展示了一系列新热带植物,包括凤梨科植物、天南星科植物、竹苹属植物和胡姬花。 其760平方米的展示区展示了国家胡姬花园特有种群中独特、罕见及屡获殊荣的配种品种和物种。陈温祥是一位成功的商人、胡姬花爱好者和慈善家。
特别值得一提的是,他培育了陈齐贤万代兰(原名Vanda
Tan Chay Yan),在1954年的切尔西花展上获得了一等证书。
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
什么是兰花分类学?(详细概述) 作者:James Simpsonin Orchids 您是否曾经想过不同类型的兰花是如何分类的?兰花是一类独特的开花植物,其分类学令人着迷。 在本文中,我们将深入探讨兰花分类学的细节,包括单子叶开花植物群概述、兰花亚科、兰花属和种的特征、不同类型的兰花、流行的兰花种类以及兰花的生长要求。 加入我们,探索兰花分类学的复杂世界。
兰花分类学概述 单子叶开花植物群 兰花亚科 兰花属和种的特征 不同类型的兰花 流行的兰花品种 兰花的生长要求 最后的想法 ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
兰花是分类学上属于天门冬目(Asparagales)的一类开花植物。它们被归类为兰科,该科又分为五个亚科:Apostasioideae、Cypripedioideae、Orchidoideae、Vanilloideae 和 Epidendroideae。这些亚科中有超过 25,000 种不同的兰花,使它们成为世界上最多样化和最丰富的开花植物科之一。 兰花分类学概述 兰花是世界上最多样化、最美丽的开花植物之一。 它们的形状、大小和颜色各异,很难分类。 为了理解大量的物种和品种,植物学家开发了一个系统的分类系统,将兰花物种分为不同的类别。 兰花分类系统的顶部分为两个亚科:Epidendroideae 和 Pleurothallidinae。这两个亚科随后进一步分为属和种。每个属和种都有自己独特的特征,例如花的结构、生长习性和叶子。 Epidendroideae 亚科是最大、最多样化的兰花亚科,包含 20,000 多种。 它包括流行的卡特兰、蝴蝶兰和兜兰。 该亚科的特点是其花具有三裂唇和单尖柱。 Pleurothallidinae 亚科是规模较小、种类较少的兰花亚科,包含 1,000 多个品种。 它包括流行的 Masdevallia、Pleurothallis 和 Restrepia 兰花。 该亚科的特点是其花具有两裂唇和多尖柱。 每个亚科内都有几个属和种,每个属和种都有自己独特的特征。 例如,在 Epidendroideae 亚科中,Cattleya、Phalaenopsis 和 Paphiopedilum 属的花结构、生长习性和叶子都不同。 同样,在 Pleurothallidinae 亚科中,Masdevallia、Pleurothallis 和 Restrepia 属都有自己独特的特征。 综上所述,兰花分类学是一种基于植物的物理和形态特征的分类系统。 它将兰花分为两个亚科,即 Epidendroideae 和 Pleurothallidinae,然后将每个亚科进一步划分为属和种。 每个属和种都有自己独特的特征,例如花的结构、生长习性和叶子。 单子叶开花植物群 兰花是一个多样化的开花植物科,自古以来就因其美丽和独特的特性而被栽培。 它们被归入一个特定的分类系统,将其置于单子叶开花植物群中。 该系统基于植物的物理和形态特征,例如花的结构、生长习性和叶子。 该分类系统用于根据植物的子叶(称为子叶)数量对植物进行分组。单子叶植物是具有单个子叶的植物,而双子叶植物是具有两个子叶的植物。单子叶植物进一步分为两个亚类:单子叶被子植物和单子叶裸子植物。兰花属于单子叶被子植物组,其特征是花朵的花瓣和萼片通常是三的倍数,并且叶子的脉络平行。 在单子叶开花植物组中,兰花进一步分为两个亚科:Epidendroideae 和 Pleurothallidinae。Epidendroideae 亚科包括最著名的兰花属,例如卡特兰、石斛和蝴蝶兰。 Pleurothallidinae 亚科的兰花较小,更精致,例如 Masdevallia 和 Pleurothallis。这些属和种中的每一个都有自己独特的特征,例如花的形状、大小、颜色和气味。 通过了解兰花的分类系统,可以更容易地识别和分类个体植物。 这有助于选择和培育单个品种,以及培育杂交品种。 了解分类系统也有助于了解兰花的进化史,以及它们如何随着时间的推移适应环境。 兰花亚科 兰花是一个多样化的开花植物科,因其美丽和独特的特性而广受欢迎。它们被归类为一个特定的分类系统,将它们置于单子叶开花植物群中。该系统基于植物的物理和形态特征,例如花的结构、生长习性和叶子。 兰花进一步分为两个亚科:Epidendroideae 和 Pleurothallidinae。 Epidendroideae 亚科包括大多数兰花物种,由 30,000 多种组成。 该亚科包括常见的属,例如蕙兰、卡特兰、蝴蝶兰和兜兰等。 这些兰花以其色彩鲜艳、香气浓郁的花朵而闻名,其中一些甚至因其药用价值而被使用。 Pleurothallidinae 亚科包括 3,700 多种兰花,包括 Masdevallia、Stelis 和 Lepanthes 等属。 这些兰花通常体型较小,花朵精致而复杂。 它们主要分布在南美雨林中,喜欢潮湿、阴凉的环境。 除了这两个亚科外,还有其他几种不属于这两个亚科的兰花属。 其中一些属是 Bulbophyllum、Epidendrum 和 Oncidium,它们因其艳丽的花朵和持久的花期而广受欢迎。 无论您选择种植哪种兰花亚科,您都可以肯定,您将收获令人惊叹的美丽和独特特征。 只要得到正确的护理和关注,这些植物可以带来多年的享受和赞美。 兰花属和种的特征 说到兰花,没有两株是完全相同的。 每种兰花属和种都有自己独特的特征,可用于识别和分类。 例如,有些兰花有大而艳丽的花朵,而另一些兰花有小而精致的花朵。 有些兰花有芳香的花朵,而另一些兰花则根本没有香味。 兰花的叶子也有很大差异,从长而窄的叶子到宽而圆的叶子。 兰花属可以进一步分为种。 种是具有相同特征的植物,它们是兰花科中最小的分类单位。 每种兰花通常通过其花形、颜色、大小和气味来识别。 有些兰花因其美丽而受到人们的青睐,而另一些兰花则因其药用价值而备受推崇。 除了物理特性外,兰花还根据其生长习性进行分类。 有些兰花是陆生的,也就是说它们生长在土壤中,而另一些兰花是附生的,生长在其他植物上。 有些兰花是常绿的,而另一些兰花是落叶的,冬天会落叶。 不同类型的兰花 兰花是一个多样化的开花植物家族,有多种形状、大小和颜色。 根据种类的不同,兰花可以在热带和亚热带地区以及温带地区找到。 它们不仅美丽,而且非常有用。 有些兰花用于药用,而另一些则用于装饰。 由于其多样性,兰花根据物理和形态特征(如花的结构、生长习性和叶子)被划分为特定的分类系统。 这个系统被称为兰花分类学。 兰花分类学分为两个亚科,即 Epidendroideae 和 Pleurothallidinae。 前者是最大的亚科,包含大多数兰花物种,而后者是一个小得多的亚科,包含的物种较少。 在这两个亚科中,有几种兰花属和种。 这些属和种都具有独特的特征,有助于将它们彼此区分开来。 例如,一些兰花有大而多彩的花朵,而另一些兰花有小而白的花朵。 一些兰花有厚而坚韧的叶子,而另一些兰花有薄而细腻的叶子。 无论您在寻找哪种兰花,一定有一种适合您的需求。 从蝴蝶兰的精致美丽到文心兰的独特纹理叶子,兰花有各种各样的形状、大小和颜色。 因此,如果您正在寻找一种独特而美丽的植物来添加到您的收藏中,请考虑研究兰花分类。 兰花有许多不同的属和种,您一定能找到最适合您的。
流行的兰花品种 兰花是最受欢迎的植物之一,因为它们美丽而独特。 兰花有成千上万种,每种都有自己独特的外观和用途。 一些最受欢迎的兰花品种包括蝴蝶兰、卡特兰、蕙兰、万代兰和石斛兰。 蝴蝶兰是一种常见的兰花品种,易于护理,花朵美丽。 这些兰花通常在家中种植,每年可开花多次。 卡特兰是一种大花品种,可产生鲜艳而美丽的花朵。 蕙兰以其艳丽的花朵而闻名,有多种颜色,包括红色、橙色、粉色和黄色。 万代兰是一种大型芳香品种,因其芳香的花朵和壮观的颜色而广受欢迎。 最后,石斛兰是一种健壮的品种,有多种颜色,通常在家中种植。 无论您选择种植哪种兰花,它们都一定会为任何家庭增添美丽和生机。在决定种植某个品种之前,了解兰花的分类系统很重要。该系统基于植物的物理和形态特征,例如花的结构、生长习性和叶子。 兰花进一步分为两个亚科:Epidendroideae 和 Pleurothallidinae。在这些亚科中,有几个属和种,每个属和种都有自己独特的特征。了解分类系统可以帮助您为家庭选择合适的兰花品种。 兰花的生长要求 兰花以难以种植而闻名,但在适当的条件下,它们可以成为任何花园中美丽而有益的点缀。 它们需要大量的专业护理,因此在尝试种植它们之前,了解它们的生长要求非常重要。 就光照而言,兰花需要明亮的间接光照,类似于森林树冠的阴影。 应将它们放置在朝南的窗户或天窗下,但要远离直射阳光。 白天温度应在 65-80F (18-26C) 之间,夜间温度应在 55-65F (12-18C) 之间。 就湿度而言,兰花在相对湿度为 40-70% 的潮湿环境中茁壮成长。 兰花需要种植在排水良好的盆栽介质中,例如树皮碎片或珍珠岩和泥炭藓的混合物。 盆栽介质应略微湿润,并在浇水之间稍微干燥。 兰花应每 7-10 天浇水一次,每 4-6 周施肥一次均衡肥料。 兰花易受害虫和疾病的侵害,因此定期检查它们是否有感染迹象非常重要。 常见害虫包括粉蚧、介壳虫和蚜虫,而常见疾病包括冠腐病、根腐病和真菌感染。 如果您发现任何这些问题,请务必迅速采取行动,以防止感染蔓延。 通过了解兰花的生长需求并提供适当的环境,您可以帮助确保您的兰花植物在未来几年内茁壮成长。 只要得到适当的照顾和关注,兰花就可以成为任何花园中令人愉悦和美丽的点缀。 最后的想法 兰花是一种迷人的开花植物,因其美丽和独特的特性而备受喜爱。 根据其物理和形态特征,它们被归类为特定的分类系统,并进一步分为两个亚科。 每种兰花都有自己独特的特征和生长要求,对于任何想要为花园增添色彩和美感的人来说,它们都是绝佳的选择。 无论您是初学者还是经验丰富的园丁,总有一款兰花适合您。 那么为什么不去探索奇妙的兰花世界并找到最适合您的兰花呢?
What is Orchids Taxonomy? (Detailed Overview) Written by James Simpsonin Orchids Have you ever wondered how different types of orchids are classified? Orchids are a unique group of flowering plants, and their taxonomy is fascinating. In this article, well dive into the details of orchid taxonomy, including an overview of the monocotyledonous group of flowering plants, the subfamilies of orchids, the characteristics of orchid genera and species, the different types of orchids, popular orchid species, and the growing requirements for orchids. Join us as we explore the intricate world of orchid taxonomy. Overview of Orchid Taxonomy Monocotyledonous Group of Flowering Plants Subfamilies of Orchids Characteristics of Orchid Genera and Species Different Types of Orchids Popular Orchid Species Growing Requirements for Orchids Final thoughts +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Orchids are a family of flowering plants classified in the Taxonomic Order Asparagales. They are classified in the family Orchidaceae, which is divided into five subfamilies: Apostasioideae, Cypripedioideae, Orchidoideae, Vanilloideae, and Epidendroideae. Within these subfamilies are over 25,000 different species of orchid, making them one of the most diverse and abundant flowering plant families in the world. Orchids are one of the most diverse and beautiful flowering plants in the world. They come in a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and colors, which can make them difficult to classify. To make sense of the vast number of species and varieties, botanists have developed a systematic taxonomic system for organizing orchid species into distinct categories. At the top of the orchid taxonomy system is the division into two subfamilies: Epidendroideae and Pleurothallidinae. These two subfamilies are then further divided into genera and species. Each genus and species has its own unique characteristics, such as flower structure, growth habits, and foliage. The Epidendroideae subfamily is the largest and most diverse orchid subfamily, containing over 20,000 species. It includes the popular Cattleya, Phalaenopsis, and Paphiopedilum orchids. This subfamily is characterized by its flowers, which have a three-lobed lip and a single-pointed column. The Pleurothallidinae subfamily is the smaller, less diverse orchid subfamily, containing just over 1,000 species. It includes the popular Masdevallia, Pleurothallis, and Restrepia orchids. This subfamily is characterized by its flowers, which have a two-lobed lip and a multi-pointed column. Within each subfamily, there are several genera and species, each with its own unique characteristics. For example, within the Epidendroideae subfamily, the genera Cattleya, Phalaenopsis, and Paphiopedilum all have different flower structures, growth habits, and foliage. Similarly, within the Pleurothallidinae subfamily, the genera Masdevallia, Pleurothallis, and Restrepia all have their own unique characteristics. In summary, orchid taxonomy is a system of classification that is based on the physical and morphological characteristics of the plants. It divides orchids into two subfamilies, Epidendroideae and Pleurothallidinae, and then further divides each subfamily into genera and species. Each genus and species has its own unique characteristics, such as flower structure, growth habits, and foliage. Monocotyledonous Group of Flowering Plants Orchids are a diverse family of flowering plants that have been cultivated since ancient times for their beauty and unique characteristics. They are classified into a specific taxonomic system, which places them in the monocotyledonous group of flowering plants. This system is based on the physical and morphological characteristics of the plants, such as flower structure, growth habits, and foliage. This classification system is used to group plants according to the number of seed leaves they have, known as cotyledons. Monocotyledonous plants, or monocots, are plants that have a single seed leaf, while dicotyledonous plants, or dicots, have two seed leaves. Monocots are further divided into two subgroups: monocotyledonous angiosperms and monocotyledonous gymnosperms. Orchids belong to the monocotyledonous angiosperm group, which are characterized by having flowers with petals and sepals that are most often in multiples of three, along with parallel-veined leaves. Within the monocotyledonous group of flowering plants, orchids are further divided into two subfamilies: Epidendroideae and Pleurothallidinae. The Epidendroideae subfamily includes the most well-known orchid genera, such as Cattleya, Dendrobium, and Phalaenopsis. The Pleurothallidinae subfamily features smaller, more delicate orchids, such as Masdevallia and Pleurothallis. Each of these genera and species within them have their own unique characteristics, such as flower shape, size, color, and scent. By understanding the taxonomic system of orchids, it is easier to identify and classify individual plants. This can help in selecting and growing individual varieties, as well as in cultivating hybrids. Understanding the taxonomic system can also help in understanding the evolutionary history of orchids, and how they have adapted to their environment over time. Orchids are a diverse family of flowering plants that are popularly grown for their beauty and unique characteristics. They are classified into a specific taxonomic system, which places them in the monocotyledonous group of flowering plants. This system is based on the physical and morphological characteristics of the plants, such as flower structure, growth habits, and foliage. Orchids are further divided into two subfamilies: Epidendroideae and Pleurothallidinae. The Epidendroideae subfamily includes the majority of the orchid species, and consists of over 30,000 species. This subfamily includes the popular genera such as Cymbidium, Cattleya, Phalaenopsis, and Paphiopedilum, among others. These orchids are known for their colorful and fragrant blooms, and some of them are even used for their medicinal properties. The Pleurothallidinae subfamily includes over 3,700 species of orchids, and includes genera such as Masdevallia, Stelis, and Lepanthes. These orchids are usually smaller in size and often have delicate, intricate flowers. They are mostly found in South American rainforests and prefer humid, shady conditions. In addition to these two subfamilies, there are also several other genera of orchids that are not classified into either of these two subfamilies. Some of these genera are Bulbophyllum, Epidendrum, and Oncidium, which are popularly grown for their showy flowers and long-lasting blooms. No matter which subfamily of orchid you choose to grow, you can be sure that you will be rewarded with a stunning display of beauty and unique characteristics. With the correct care and attention, these plants can provide years of enjoyment and admiration. Characteristics of Orchid Genera and Species When it comes to orchids, no two are exactly alike. Each genus and species of orchid has its own unique set of characteristics, which can be used to identify and classify them. For example, some orchids have large, showy flowers, while others have small, delicate blooms. Some orchids have fragrant flowers, while others have no scent at all. The foliage of orchids also varies greatly, ranging from long, narrow leaves to broad, rounded ones. Orchid genera can be further divided into species. Species are plants with the same characteristics, and they are the smallest unit of classification in the orchid family. Each species of orchid is typically identified by its flower shape, color, size, and scent. Some species are grown for their beauty, while others are prized for their medicinal properties. In addition to physical characteristics, orchids are also classified based on their growth habits. Some orchids are terrestrial, meaning they grow in soil, while others are epiphytic and grow on other plants. Some orchids are evergreen, while others are deciduous and lose their leaves in the winter. Orchids are a diverse family of flowering plants that come in many shapes, sizes, and colors. Depending on the species, orchid plants can be found in tropical and subtropical regions, as well as temperate zones. Not only are they beautiful, but they are also quite useful. Some orchids are used for medicinal purposes, while others are used for decoration. Due to their diverse nature, orchids are classified into a specific taxonomic system, based on physical and morphological characteristics, such as flower structure, growth habits, and foliage. This system is known as orchids taxonomy. Orchids taxonomy is divided into two subfamilies, Epidendroideae and Pleurothallidinae. The former is the largest subfamily, containing the majority of orchid species, while the latter is a much smaller subfamily, containing fewer species. Within these two subfamilies, there are several genera and species of orchids. These genera and species all have unique characteristics that help distinguish them from each other. For example, some orchids have large, colorful blooms, while others have small, white flowers. Some orchids have thick, leathery leaves, while others have thin, delicate foliage. No matter what type of orchid you are looking for, there is sure to be a species that fits your needs. From the delicate beauty of the Phalaenopsis orchid to the unique, textured leaves of the Oncidium orchid, orchids come in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and colors. So, if you are looking for a unique and beautiful plant to add to your collection, consider looking into orchids taxonomy. With the many different genera and species of orchids, you are sure to find the perfect one for you. Orchids are one of the most popularly grown plants, due to their beauty and unique characteristics. There are thousands of species of orchids, each with its own distinct look and purpose. Some of the most popular species of orchids include the Phalaenopsis orchid, Cattleya orchid, Cymbidium orchid, Vanda orchid, and Dendrobium orchid. The Phalaenopsis orchid is a common species of orchid that is easy to care for and produces lovely blooms. These orchids are popularly grown in the home and can bloom multiple times a year. The Cattleya orchid is a large-flowered species that produces vibrant and stunningly beautiful blooms. Cymbidium orchids are known for their showy flowers and can be found in a variety of colors, including red, orange, pink, and yellow. The Vanda orchid is a large, fragrant species that is popularly used for its fragrant blooms and spectacular colors. Finally, the Dendrobium orchid is a robust species that can be found in a variety of colors and is popularly grown in the home. No matter which species of orchid you choose to grow, they are sure to add beauty and life to any home. Before you decide on a particular species, its important to understand the orchids taxonomic system. This system is based on the physical and morphological characteristics of the plants, such as flower structure, growth habits, and foliage. Orchids are further divided into two subfamilies: Epidendroideae and Pleurothallidinae. Within these subfamilies, there are several genera and species, each with its own unique characteristics. Understanding the taxonomic system can help you choose the right species of orchid for your home. Growing Requirements for Orchids Orchids are notoriously difficult to grow, but with the right conditions, they can be a beautiful and rewarding addition to any garden. They require a lot of specialized care, so it’s important to understand their growing requirements before attempting to cultivate them. When it comes to lighting, orchids need bright, indirect light that mimics the shade of a forest canopy. They should be placed in a south-facing window or under a skylight, but away from direct sunlight. The temperature should range between 65-80F (18-26C) during the day and between 55-65F (12-18C) at night. When it comes to humidity, orchids thrive in a humid environment of 40-70% relative humidity. Orchids need to be planted in a well-draining potting medium, such as bark chips or a combination of perlite and peat moss. The potting medium should be lightly moist and allowed to dry slightly between watering. Orchids should be watered every 7-10 days and fertilized with a balanced fertilizer every 4-6 weeks. Orchids are susceptible to pests and diseases, so it’s important to inspect them regularly for signs of infestation. Common pests include mealybugs, scale, and aphids, while common diseases include crown rot, root rot, and fungal infections. If you notice any of these problems, it’s important to take action quickly to prevent the spread of the infection. By understanding the growing needs of orchids and providing the right environment, you can help ensure that your orchid plants thrive for years to come. With the right care and attention, orchids can be a rewarding and beautiful addition to any garden.
Orchids are a fascinating family of flowering plants that are beloved for their beauty and unique characteristics. They are classified into a specific taxonomic system based on their physical and morphological characteristics, and further divided into two subfamilies. Each orchid species has its own unique characteristics and growing requirements, making them a great choice for anyone looking to add some color and beauty to their garden. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced gardener, there’s an orchid out there that is perfect for you. So why not explore the wonderful world of orchids and find the perfect one for you? |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
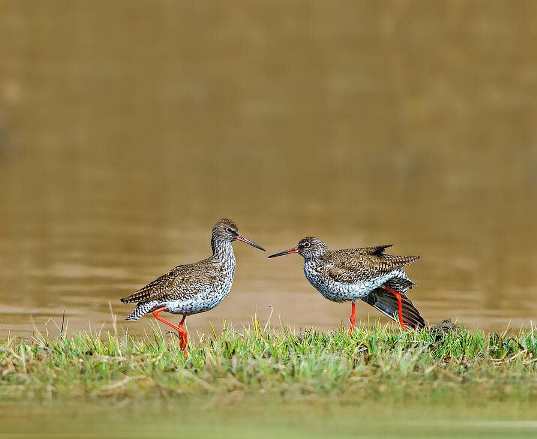 红脚鹬Common Redshank Hóng jiǎo yù |
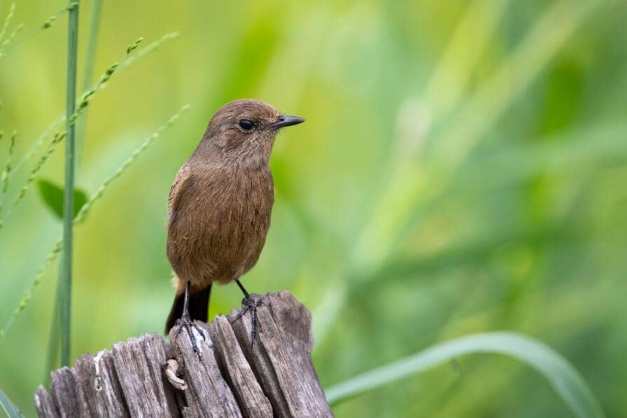 棕胸丛林霸鹟 Brown-breasted Flycatcher cōng xiōng cónglín bà wēng |
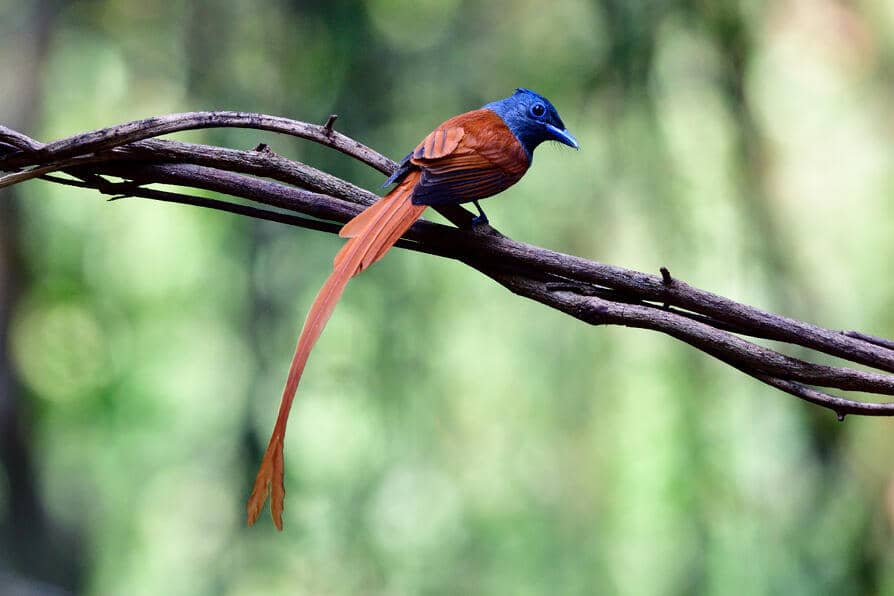 红胸天鹟 Paradise flycatcher Hóng xiōng tiān wēng |
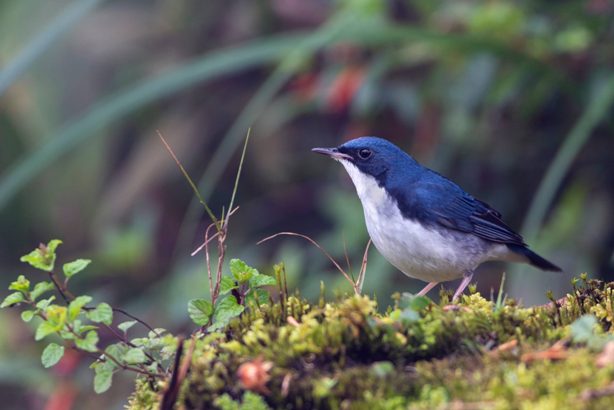 蓝知更鸟 Robin Lán zhī gēng niǎo |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
亚洲长嘴鹬 asian long bill sandpiper/Asian Dowitcher,
|
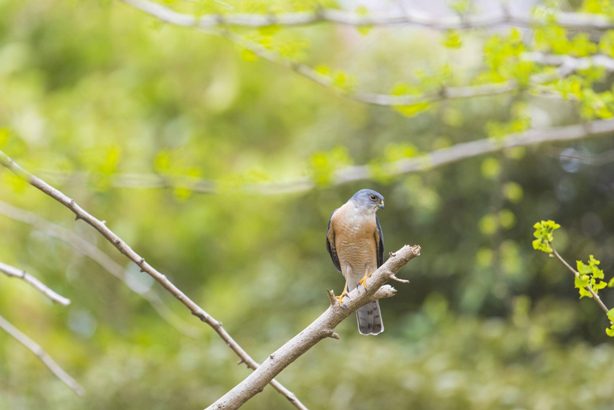 日本雀鹰 Rìběn què yīng |
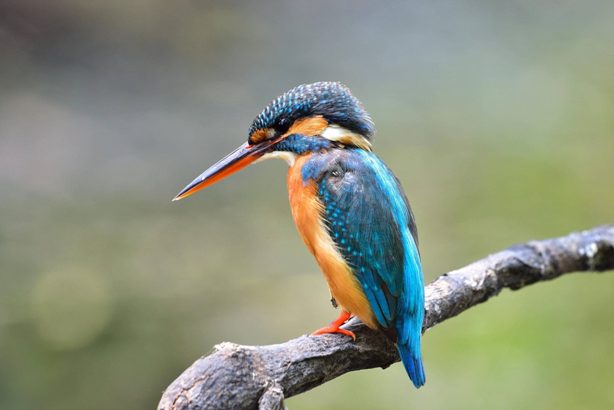 翠鸟Cuì niǎo |
 凤头蜂鹰 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
2022 年 5 月 12 日
据专家介绍,这一数字翻倍可能是由于迁徙模式的变化、气候变化,或者仅仅是因为自 Covid-19 疫情爆发以来,观鸟者越来越多。
在新加坡 9 月至 4 月的候鸟季节,请务必随身携带这篇文章! 保护区内有无数的候鸟,这是您在观鸟冒险中绝对不能错过的一个地方! 这些鸟来自俄罗斯远东地区、蒙古和中国,通常是最早抵达新加坡的鸟类之一,从
7 月初开始,人们就会在我们阳光明媚的岛屿上看到它们。
繁殖时为砖红色,不繁殖时为灰褐色。
蜂鹰会拆毁蜜蜂和黄蜂的巢穴,以幼虫为食,这是掠食性鸟类中相对独特的行为。蜂鹰体长可达 65
厘米,与普通鸟类相比体型巨大,头部小巧,类似鸡头,很容易辨认。蜂鹰是新加坡冬季最常见的候鸟之一,经常成群结队。 |
12 MAY 2022 4 Places in Singapore to catch a glimpse of Migratory Birds Birds form a big part of our biodiversity and ecosystem here in Singapore with over 300 native bird species. Each year, the country also sees a wide range of birds passing through during migratory seasons, a spectacular sight for the growing community of birdwatchers (otherwise known as birders) in Singapore. Last year, there was also an increase in the number of rare birds sighted in the country with 12 never-seen-before birds. According to experts, the doubling of this figure could be attributed to the change in migratory patterns, climate change, or simply because there are more birdwatchers since the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic. In line with World Migratory Birds Day that falls annually 14 May, we’ve rounded up the various places that offer the best spots to observe our transient visitors. Do keep this article handy during Singapore’s migratory bird season between September to April!
1. Sungei Buloh Wetland Reserve Recognised as a site of international importance for migratory birds, Sungei Buloh Wetland Reserve was been awarded by the Wetlands International in 2002, marking the reserve’s formal entry into the East Asian Australasian Shorebird Site Network. Since then, Sungei Buloh has expanded to include a wider area of mangroves, mudflats, ponds, and forests, providing an even greater sanctuary for the rich biodiversity it supports. With a myriad of migratory birds at the reserve, this is one location that you simply cannot skip in your birdwatching adventure! One of the most common birds you can spot at the reserve is the Common Redshank, otherwise known by its scientific name Tringa Totanus. Characterised by their distinctive bright orange-red legs and relatively long stout bill, these medium-sized grey-brown birds are a common sight at the reserve between August and April. These birds come a long way from Russian Far East, Mongolia, and China and are often one of the first arrivals in Singapore, with sightings on our sunny island from early July. Besides the Common Redshank, do also keep your eyes peeled for the Asian Dowitcher, a beautiful species that changes the colour of its feathers depending on its breeding season – brick-red when breeding and greyish-brown when not. Given that there are only about 23,000 Asian Dowitchers left globally, it is listed as Near Threatened on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) red list of threatened species. Travelling from as far as southern Siberia, these birds typically only stop over at the wetland reserve for just one day, so you’ll have to be really lucky to spot one of these elusive creatures!
2. Jelutong Tower at MacRitchie Reservoir One of the best places in Singapore to spot migratory birds, and a favourite among avid birdwatchers, will definitely be the Jelutong Tower located within MacRitchie Reservoir. In addition to spotting a variety of birds, make your way up the seven-deck observation tower and be treated to an unblocked view of the forest canopy MacRitchie has to offer. While the nondescript Brown-chested Jungle Flycatcher might be easily brushed off as one of many similar-looking brown birds in the Southeast Asia region, a seasoned birder would know how rare it is to spot one given its globally threatened status. Although there are only a handful of records noting the sightings of this bird in Singapore, the Central Catchment Forest is found to be one of the hotspots where they have been spotted before. Listen hard for a short series of “ticks”, a call made by the Brown-chested Jungle Flycatcher when it is alarmed, and you may have the luck to spot one of these little birdies! Another migratory bird to look out for at the Jelutong Tower is the eye-catching Siberian Blue Robin. With the males of this species boasting royal blue upperparts and snow-white underparts, it is easily spotted amongst the green canopies. In addition to Siberia, this blue robin also breeds in Mongolia, Korea, China and Japan before travelling thousands of kilometres to warmer parts of Southeast Asia to tide over for winter – a formidable distance for such a small bird! With the rich biodiversity found in MacRitchie Reserve, don’t forget to also keep a look out for other wildlife at the Jelutong Tower, such as the critically endangered Raffles Banded Langur and Sunda Pangolin.
3. Hampstead Wetlands Park Located at Seletar Aerospace Park, Hampstead Wetlands Park is well-known as a green sanctuary for wildlife. Centred around a freshwater lake, the park offers birds and other animals with shelter, resting grounds and nesting spots, away from predators and human disturbances. With its array of birds, Hampstead Wetlands Park is the perfect spot if you’re a beginner birder. One of the most magnificent species you can find at the park is The Crested Honey Buzzard otherwise also known as the Oriental Honey Buzzard. While an excellent hunter, this raptor specialises in dismantling the nests of bees and wasps to feed on their larvae, a relatively unique behaviour amongst predatory birds. Sizing up to 65 centimetres, the Crested Honey Buzzard are massive compared to your average birds and can be easily identified with its small chicken-like head. As one of the most common migrants in Singapore during the winter season, they can be often seen travelling in a group. Another interesting bird easily spotted at Hampstead Wetlands Park is the Japanese Sparrowhawk – the most common accipiter in Singapore. This species of bird is widespread throughout Singapore during the winter months and can be often seen soaring in the skies. If you’re lucky, you can even watch them in action at the freshwater lake at the park hunting at low levels for their prey! In addition to birds, Hampstead Wetlands Park is also home to a wide range of flora and fauna so do keep your eyes peeled for some unique species, such as the Buffy Fish Owl as you take a leisure stroll along the scenic boardwalk.
4. Jurong Lake Gardens The newest Singapore national gardens on our little island, Jurong Lake Gardens is a 90-hectare space that is teeming with wildlife given that it houses several ecosystems including a swamp, grassland, and freshwater lake. It is therefore no surprise that Jurong Lake Gardens has been the site for “star sightings” such as the Amur Paradise Flycatcher and Oriental Dwarf Kingfisher, both notoriously difficult to spot migratory birds. Similar to many male birds of other species, the males of the Amur Paradise Flycatcher boast a distinctive look during breeding season. In this case, the tail of the adult male can extend up to 27cm or more, a striking feature for this species of birds. Unfortunately, this is rarely seen in Singapore given that they typically breed in other parts of the world before visiting Singapore to spend the winter months. With a preference to forage high up in the canopies, do remember to keep your gaze up if you’d like to spot any of these unique birdies! And while you’re at Jurong Lake Gardens, do also look out for some of the most interesting birds in nature – the kingfishers. True to their name, kingfishers are a master fisher that swoop down to catch its prey with pinpoint accuracy. With many of them conspicuously coloured, it is fairly easy to spot one from afar! One of which is the Common Kingfisher, a miniature kingfisher about the length of a small ruler that is a frequent migrant to Singapore. With its diet made up of predominantly fish, these birds can often be seen perched on branches not too far from waterbodies as they survey the landscape for their next prey. In addition to looking out for their turquoise-coloured upperparts and orange underparts, listen up for their distinctive high-pitched “tseep” that may just point you to where you can spot these beautiful birds in action! Excited to head out for your birdwatching adventure? Here are some quick tips to keep in mind as you lace up your walking shoes and head outdoors: Dress in comfortable light-coloured clothes, preferably with long sleeves to minimise any mosquito bites Bring along your own bottled water to stay hydrated Have a comfortable pair of shoes to walk in, especially if you are trekking at the same time Remember to leave any nesting birds alone, should you encounter one As we eagerly wait for the first flock of migratory birds to arrive in September, feel free to also check out Singapore Bird Project that offers an array of information about the different bird species found in our little red dot! In celebration of the magnificent array of biodiversity, let us appreciate by conserving our resident and migratory wildlife for future generations to enjoy.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||

.png)

.jpg)
.png)
.jpeg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)






.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)











.jpg)





.jpeg)
.jpg)
.png)
.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
